

Last updated on

The emergence of Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE) marks a paradigm shift in online search, heralding a fresh era of contextual understanding and intuitive information exploration.
This technological leap is reshaping SEO strategies at their core, necessitating a paradigm shift in content development methodologies.
The impact on end-users is profound, with AI significantly streamlining access to search outcomes.
This article advocates for an advanced thematic mapping strategy to optimize the efficacy of these technological advancements in SEO.
Furthermore, it delves into the capabilities and constraints of large language models (LLMs) such as OpenAI’s GPT, Google’s Bard, and Microsoft’s Bing AI, shedding light on their potential and limitations in the realm of SEO content generation.
The introduction of Google SGE represents a groundbreaking transformation in online search. This advancement reflects Google’s adoption of a more contextual and intuitive method for retrieving information.
This evolution necessitates a reevaluation of how SEO professionals strategize and plan their content approaches.
Moreover, the user experience undergoes a notable evolution, with AI-driven search outcomes becoming more readily accessible.
Answers are swiftly attainable, eliminating the need to navigate through numerous tabs and pages.
Grasping the mechanics of this AI technology and employing novel techniques to extract its insights are imperative for effectively positioning oneself and comprehending its constraints.
Large language models (LLMs) like GPT, Bard, and Bing AI wield considerable prowess in natural language generation and comprehension.
Nonetheless, these models grapple with constraints, particularly in grasping nuanced contexts and ensuring real-time information updates.
It’s imperative for SEO project teams to grasp these limitations to optimize their content creation endeavors.
Knowledge can be categorized into two realms: firstly, data employed for training, and secondly, information indexed within the search engine, integral to generating responses.
To elucidate this concept, allow me to demonstrate how we can effectively map this knowledge.
Thematic mapping stands as a pivotal instrument in SEO, orchestrating and framing content in a coherent and intuitive manner.
This method guarantees the thorough coverage of all aspects of a subject, thereby enhancing the relevance and caliber of the content. Leveraging an LLM for thematic mapping confers distinct advantages in fostering fresh ideas and viewpoints.
The Structural Framework of a Thematic Map
Thematic mapping entails the amalgamation of interconnected ideas and subjects into clusters, facilitating the development of coherent and exhaustive content.
This approach not only streamlines the organization of ideas in a rational manner but also aids in pinpointing deficiencies within current content repositories.
Choice Of Topic And Keywords
Selecting a niche topic and determining relevant keywords is essential for effective content creation and search engine optimization. While various approaches exist, I recommend utilizing Google’s AI, particularly PaLM 2, if you’re proficient with Google’s tools. (Note: I’ve established a training course on Data Marketing Labs for your reference).
To initiate this process using ChatGPT, here’s a streamlined prompt:
“Generate a table listing ontologies related to ‘YOUR CONCEPT.'”
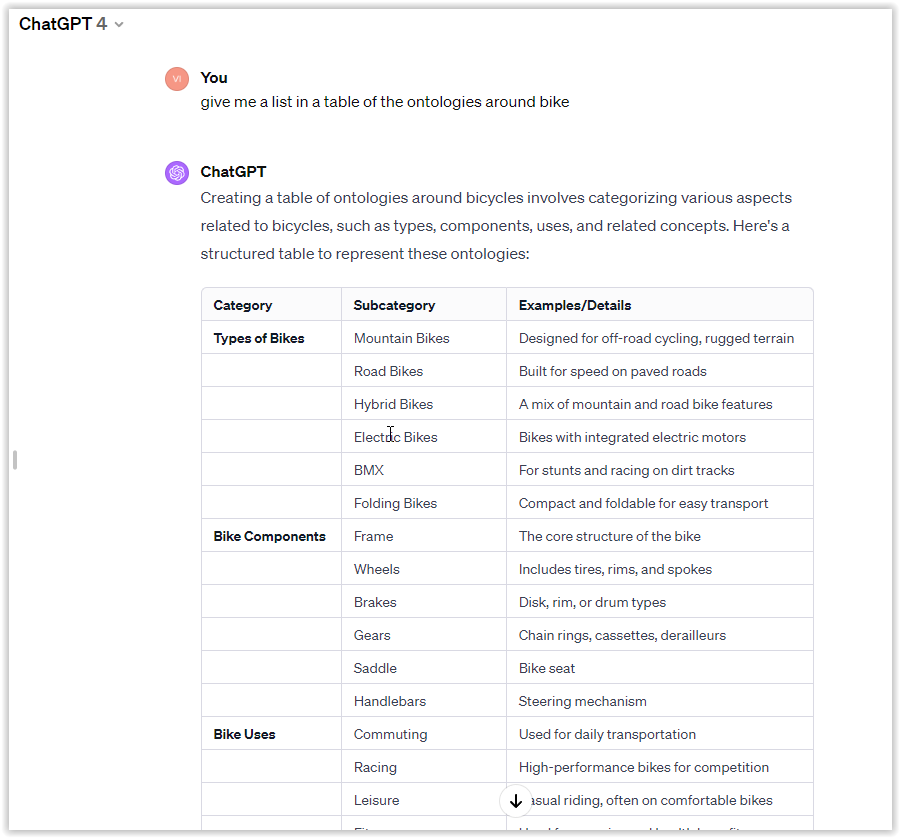
Brainstorming
When brainstorming with the LLM, requesting multiple passages for each expression is beneficial for several reasons. Firstly, it allows for exploration of various creative thresholds and potential responses present in Google’s index. Secondly, the LLM may offer slightly different perspectives or insights in each passage, expanding the range of possibilities for content creation. This approach ensures comprehensive coverage of the chosen topic, leveraging the expertise of tools like PaLM 2 to generate relevant and sought-after topics by web users. The more topics requested, the broader the scope and depth of exploration into the subject matter.
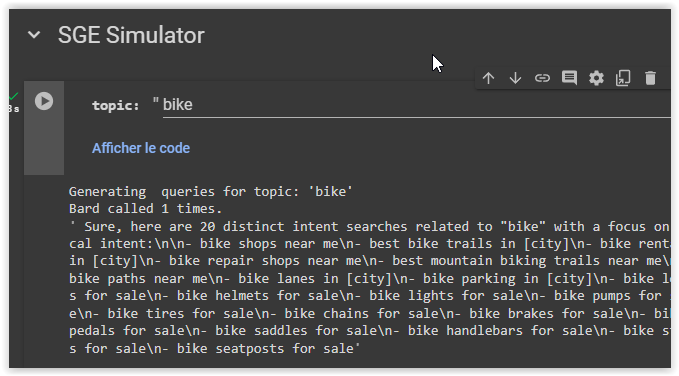
Extraction
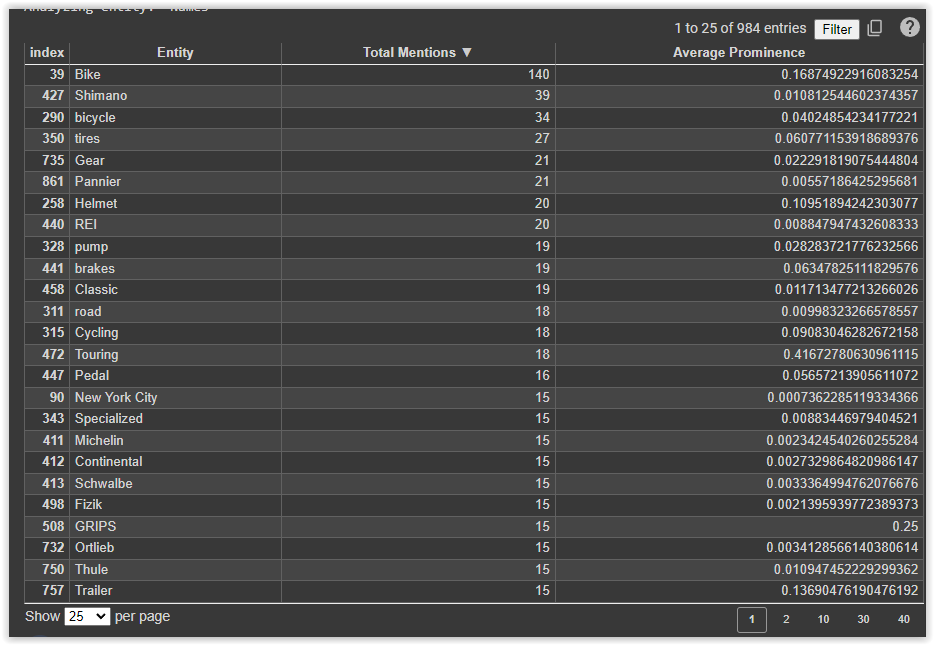
Initially, Python libraries were utilized for this task, but now, leveraging an LLM suffices due to its adeptness in handling such straightforward tasks.
Ultimately, all data is organized within an array, enabling the straightforward tallying of occurrences pertaining to a particular concept. Allow me to elaborate further on this aspect.
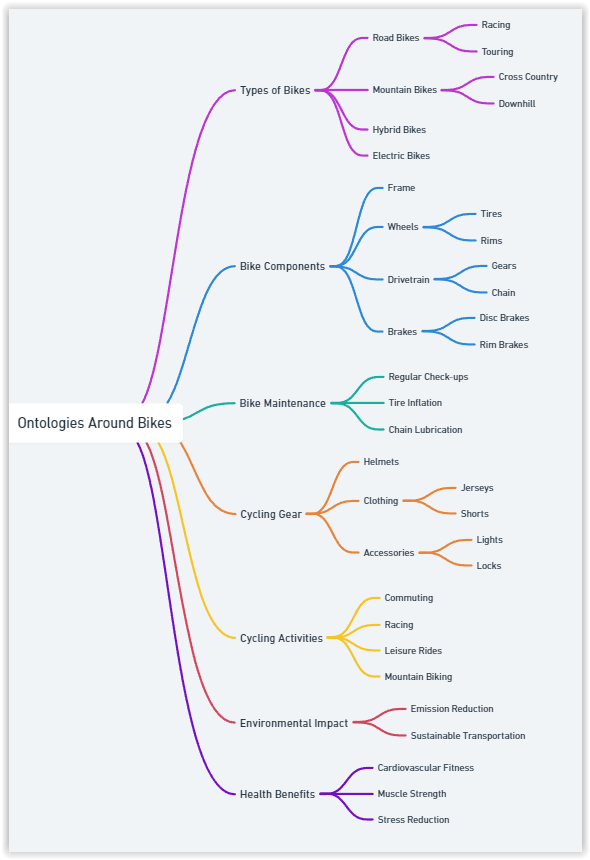
Within this visual representation, you’ll observe a systematic approach wherein five iterations are conducted for each preceding topic, facilitating the retrieval of pertinent elements crucial for constructing the mind map.
Subsequently, PaLM 2 is employed to extract significant terms from each generated text, with the entirety of this information neatly stored within a table.

As evident, each stage unfolds within Google Colab, offering readily accessible tables and simplifying data sorting with just a few clicks.
Following this, you can generate the thematic map based on this prompt.
Here’s a potential outcome:
Step 1: Creation of Thematic Map
Theme: Bicycles
Nouns/Predicates:
1. Types of Bicycles
2. Bicycle Components
3. Bicycle Activities
4. Bicycle Accessories
5. Bicycle Safety
Step 2: Semantic Graph
| Subtopic 1 | Subtopic 2 | Semantic Connection |
|---|---|---|
| Peloton bike | Electric bike | Both are bike types powered by electricity. |
| Electric bike | Sound bike boy bell | Both are components that can be added to a bike. |
| Sound bike boy bell | Human fully aware bike | Both relate to rider safety. |
| Human fully aware bike | Run walk bike regularly | Both involve physical activity associated with biking. |
| Run walk bike regularly | Mountain bike tires | Both relate to the terrain suitable for biking. |
| Mountain bike tires | Road bike pedals | Both are bike components. |
| Road bike pedals | Bike clips | Both are bike components. |
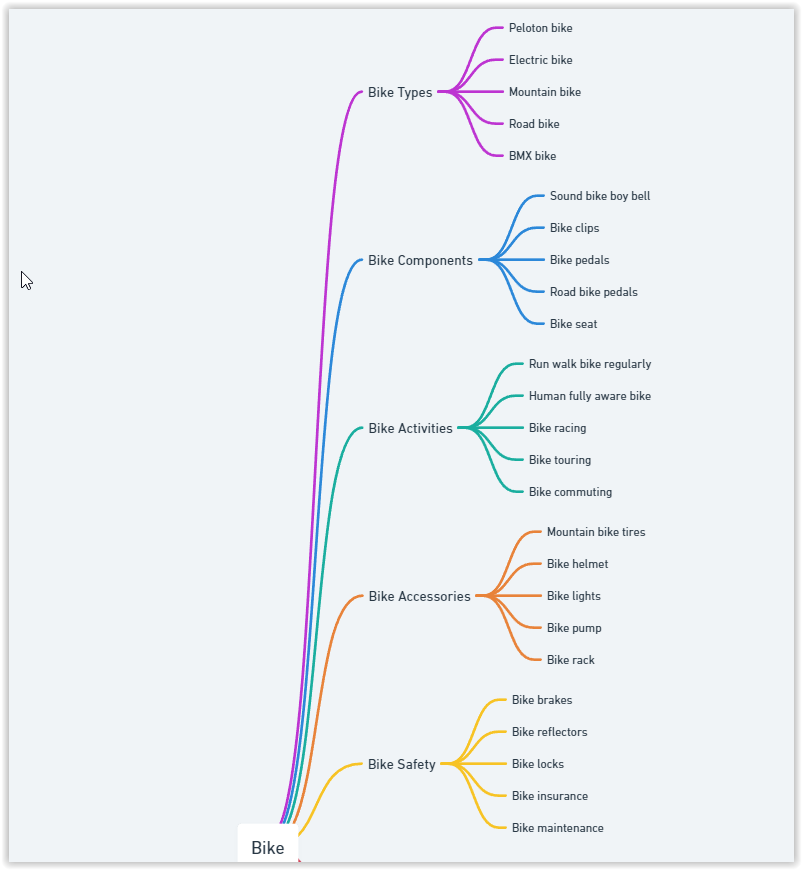
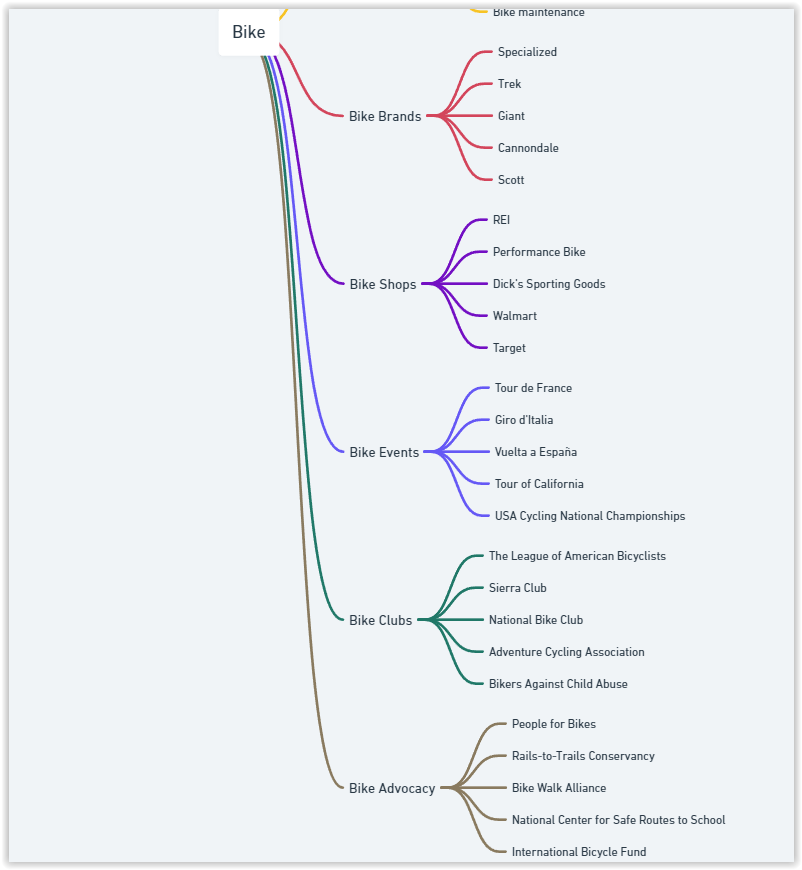
Step 3: Mind Map
Topic: Bike
Subcategories:
Visualization
Utilizing mind-mapping tools facilitates comprehensive visualization, yielding highly informative outcomes.
For seamless visualization, you can access the AI Diagrams Assistant within ChatGPT for free.
Feel free to explore and generate a mind map based on the previous steps’ data table.
Now, let’s delve into some advanced strategies to preempt Google’s SGE.
Utilize Google’s PaLM 2 to ensure comprehensive coverage of your topic within the map.
Integrate the map seamlessly into your content research and writing workflow.
Transform each sub-theme into various forms of content, such as web pages or blog posts, and interlink them to establish a cohesive network of content.
This approach offers a robust method for understanding the significance of generative AI in search engines and optimizing for generative AI search functionalities.
It incorporates detailed examples and explanations, focusing not only on topic optimization but also on prioritizing content quality and catering to specific search intents.
Human intervention remains indispensable for discerning search intent and maintaining content quality.
The collaboration between a skilled writer and AI can augment content optimization efforts, leveraging tools to enhance the efficiency and relevance of your content ecosystem.
With the emergence of generative AI, any SEO professional can construct their own toolkit.
Original news from SearchEngineJournal